Introduction:
While magnesium is essential for many bodily functions, getting the right amount isn’t just about consuming magnesium-rich foods. How well your body absorbs this mineral can depend on various factors. In this article, we’ll explore what can hinder or help magnesium absorption and how you can optimize your intake for maximum health benefits
Factors That Hinder Magnesium Absorption:
Several factors can reduce the body’s ability to absorb magnesium effectively, including certain lifestyle habits, medications, and the presence of specific nutrients. Here’s what you should know:
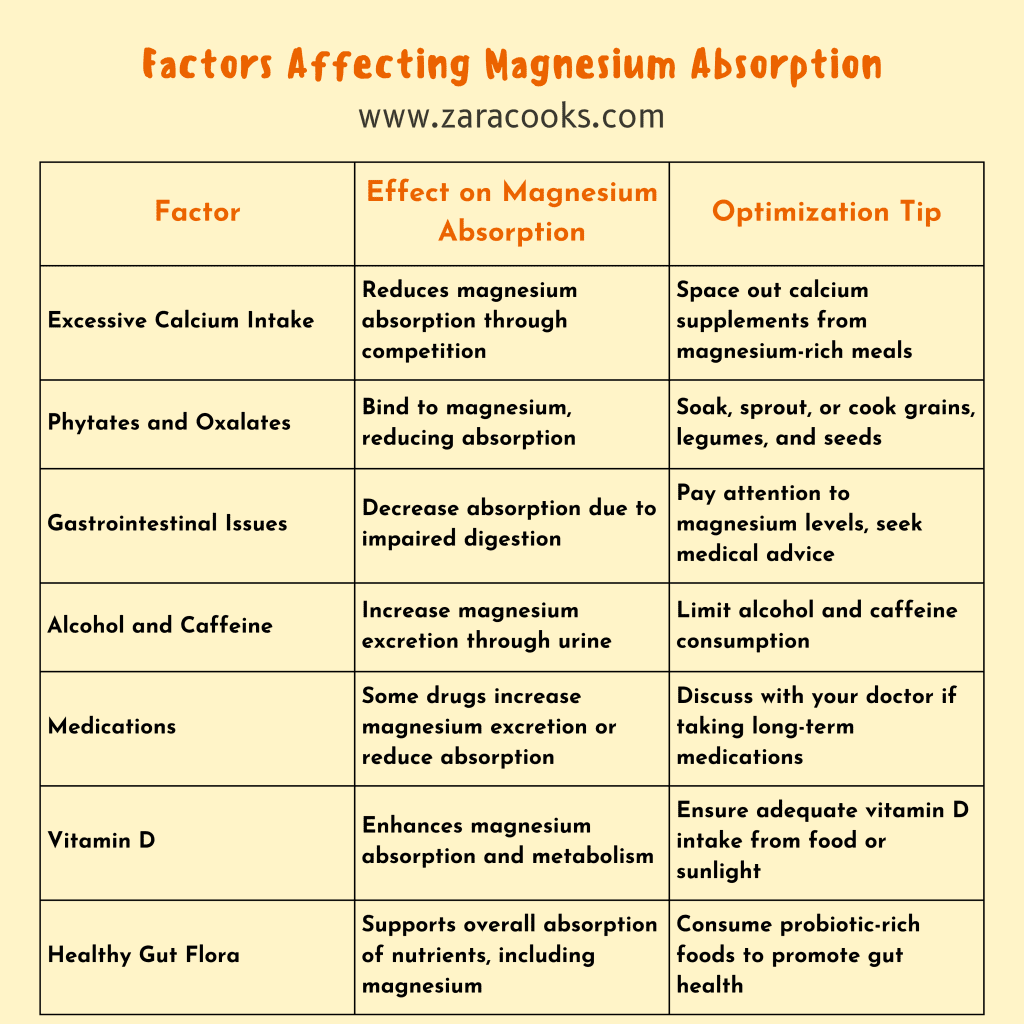
- Excessive Calcium Intake: While both calcium and magnesium are vital minerals, they compete for absorption in the intestines. A high intake of calcium, especially from supplements, can interfere with magnesium absorption. If you’re taking calcium supplements, make sure to space them out from magnesium-rich meals.
- High Phytate and Oxalate Diet: Phytates (found in grains, legumes, and seeds) and oxalates (found in leafy greens like spinach) can bind to magnesium in the gut, making it harder for the body to absorb. This is similar to the effect these compounds have on iron absorption. Although these foods are healthy, it’s important to prepare them in ways that reduce phytates and oxalates (e.g., soaking, sprouting).
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Digestive problems such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and irritable bowel syndrome can lead to poor magnesium absorption. People with these conditions may need to pay extra attention to their magnesium levels.
- Alcohol and Caffeine: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to increased magnesium excretion through urine, while caffeine may also reduce magnesium levels by acting as a diuretic. Reducing alcohol and caffeine intake can help maintain adequate magnesium levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and antibiotics, can decrease magnesium absorption or increase magnesium excretion. If you’re taking these medications long-term, talk to your doctor about monitoring your magnesium levels.
Factors That Promote Magnesium Absorption:
Fortunately, there are many ways to improve magnesium absorption. Here are some effective strategies:
- Adequate Vitamin D Levels: Vitamin D plays a key role in magnesium metabolism. It helps increase intestinal absorption of magnesium. To boost your magnesium absorption, ensure you’re getting enough vitamin D through sunlight exposure, foods like fatty fish, or supplements if needed.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in protein and healthy fats, along with magnesium, can improve its absorption. Protein helps to transport magnesium across the gut lining, enhancing its bioavailability.
- Healthy Gut: Maintaining good gut health is essential for magnesium absorption. Eating probiotic-rich foods (like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kefir) can improve gut flora, making it easier for the intestines to absorb magnesium. Additionally, fiber-rich foods help promote digestive health and may support magnesium uptake.
- Splitting Doses: If you’re taking magnesium supplements, splitting your intake into smaller doses throughout the day can help with better absorption. Large doses at once may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort and less efficient absorption.
How to Optimize Your Magnesium Intake:
- Consume Magnesium with Vitamin D: Foods that are rich in both magnesium and vitamin D—like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs—are great for maximizing absorption. If you’re taking vitamin D supplements, make sure your magnesium intake is sufficient to aid the vitamin’s activation.
- Incorporate Probiotics: Including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can support a healthy gut environment, which is key for better magnesium absorption.
- Reduce Intake of Magnesium Blockers: Avoid consuming magnesium-rich meals with foods high in phytates or oxalates (e.g., raw spinach or large amounts of nuts). Instead, soak or sprout grains, legumes, and seeds to reduce their phytate content.
- Moderate Alcohol and Caffeine: Keeping alcohol and caffeine consumption in check can help prevent magnesium depletion. Enjoy these beverages in moderation, and avoid consuming them with magnesium-rich meals.
Summary Table: Factors Affecting Magnesium Absorption
By understanding the factors that can affect magnesium absorption, you can make smarter choices about your diet and lifestyle to ensure you’re getting enough of this essential mineral. In the next article, we’ll provide a comprehensive guide to magnesium-rich foods, both vegan and non-vegan, to help you meet your daily needs.
