Introduction:
Although potassium doesn’t get as much attention as other minerals like calcium or iron, it plays a starring role in your body’s daily operations. It works quietly behind the scenes—helping your heart beat, your muscles move, and your nerves fire signals with precision. Without enough potassium, even the most basic cellular functions can start to unravel.
Let’s explore why potassium is so essential and how it keeps your body in balance.
Potassium and the Heart: A Pulse You Can Count On
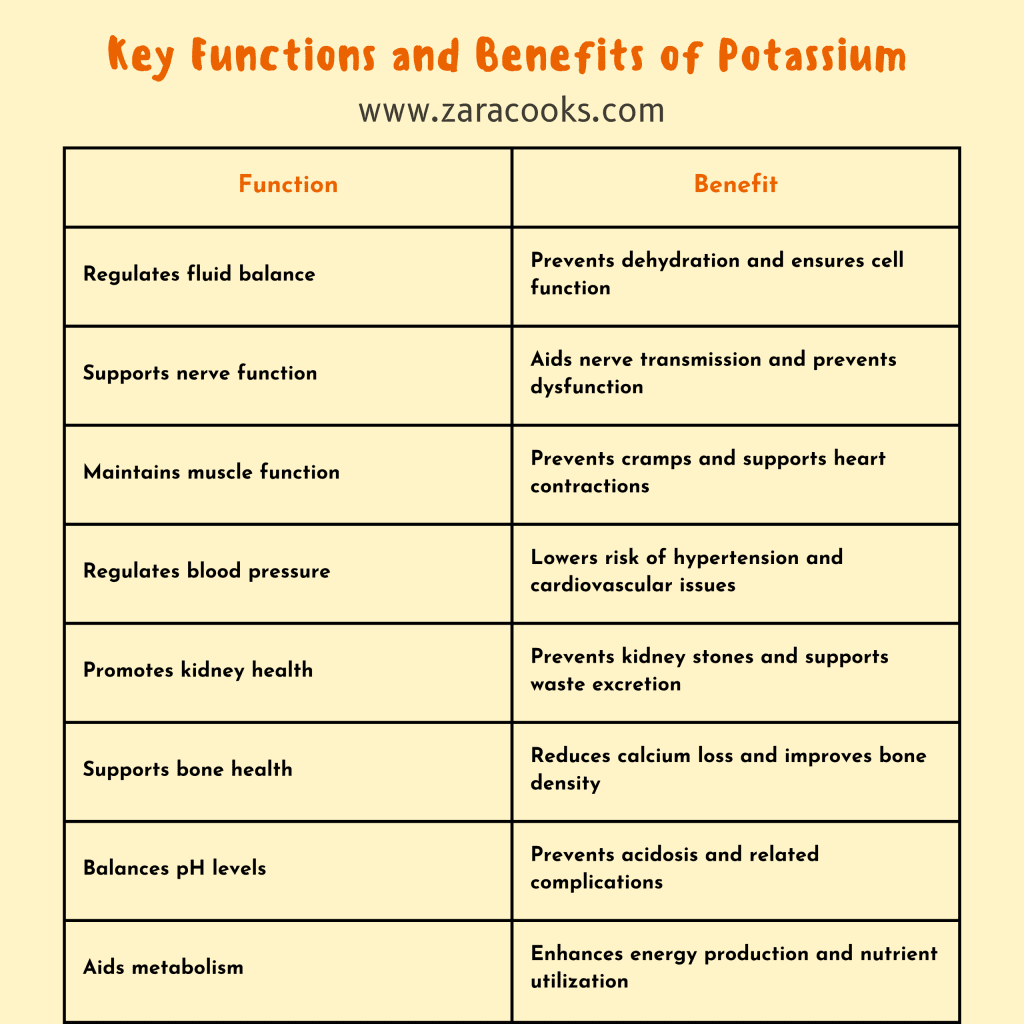
Your heart relies on electrical signals to maintain a steady rhythm. Potassium helps generate those signals, making it crucial for a healthy heartbeat. One of its key roles is balancing the effects of sodium, which in excess can increase blood pressure. Potassium helps the blood vessels relax and improves circulation, reducing strain on the cardiovascular system. In short, potassium keeps your heartbeat stable and your blood pressure in check.
Potassium and the Muscles: Moving with Ease
Every time you take a step, stretch your arm, or lift a grocery bag, potassium is helping make it happen. It’s deeply involved in muscle contractions and relaxation. Without enough potassium, muscles may become weak, feel fatigued, or cramp unexpectedly. That’s because potassium is responsible for sending the messages from your nerves that tell your muscles when and how to move.
Potassium and the Nervous System: Instant Communication
Think of your nervous system as a highway of electrical signals. Potassium is the mineral that keeps traffic flowing smoothly. It helps nerve cells send signals across the body, allowing for instant communication between your brain and muscles. Whether you’re reacting to a hot surface or catching your balance, potassium is there—quietly powering your reflexes.
Conclusion
Potassium may not be a spotlight nutrient, but it’s a quiet powerhouse regulating vital functions that keep you alive and thriving. In the next article, we’ll explore what happens when potassium levels dip too low, and the symptoms you should watch for.
